Hot Rolled Plate is a crucial material in various industries, playing a significant role in construction and manufacturing. According to recent industry reports, the demand for hot rolled steel products is projected to rise steadily. By 2025, global consumption could reach over 1.3 billion tons annually. This rising demand highlights the importance of understanding the best uses and types of hot rolled plates.
In the construction sector, hot rolled plates are often utilized in structural applications. They offer essential strength and durability, making them ideal for beams and columns. Additionally, hot rolled plates are crucial in manufacturing heavy machinery, where stability and resistance to deformation are vital. However, there can be challenges, such as warping during the cooling process, which needs careful management.
As industries adapt to evolving standards, the versatility of hot rolled plates shines through. While they can be used in various applications, a reflective approach is necessary. Factors like cost efficiency and environmental impact remain critical. Investigating these elements allows for smarter decisions in selecting the right hot rolled plate for each specific need.
Hot rolled plates are crucial in various industries. They are defined as steel plates produced at high temperatures. This process alters their internal structure, making them malleable and easy to shape. Industry reports suggest that hot rolled plates retain high levels of strength, which allows them to be molded for construction and manufacturing needs.
Characteristics include a rough surface finish and less precise dimensions when compared to cold rolled options. The typical thickness ranges from 0.5 inches to 8 inches. This makes them ideal for applications like structural beams and automotive parts. Their versatility cannot be overstated, especially in heavy machinery. However, uneven surfaces can pose challenges during later finishing processes.
Tips: When sourcing hot rolled plates, consider specifications that align with project needs. Evaluate the expected load and structural design before choosing thickness. Skipping these steps might lead to an improper fit or insufficient strength. Making informed choices ensures the longevity and safety of the final application.
| Type of Hot Rolled Plate | Thickness Range (mm) | Common Uses | Material Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Hot Rolled Plate | 5 - 40 | Construction, general machining | Good ductility, weldability, and formability |
| High Strength Hot Rolled Plate | 3 - 20 | Heavy machinery, off-shore structures | Enhanced strength and durability |
| Low Alloy Hot Rolled Plate | 5 - 25 | Automotive applications, pressure vessels | Improved toughness and hardenability |
| Corrosion Resistant Hot Rolled Plate | 6 - 30 | Marine applications, chemical containers | High resistance to corrosion and oxidation |
Hot rolled plates are essential in various industries. They come in different types and specifications. Commonly, they are categorized into structural, commercial, and hardox plates. Each type serves unique purposes. Structural hot rolled plates are often used in construction and heavy machinery. They provide a solid foundation and support.
Commercial hot rolled plates are versatile. They can be used in automotive parts, appliances, and furniture. These plates are generally less expensive and easier to work with. Hardox plates, known for their toughness, are ideal for high-wear applications, such as mining and construction.
Tips: When selecting hot rolled plates, consider the intended use. Think about durability, weight, and thickness. Not all plates are fit for every job. Check specifications carefully before purchasing. Remember, a poorly selected plate can lead to structural failures.
Keep in mind the rolling process affects the final properties. The thickness and width can vary significantly. Your choice may impact costs and performance. Sometimes, opting for a lesser-known variant might yield better results. Always revisit your choices and learn from past experiences.
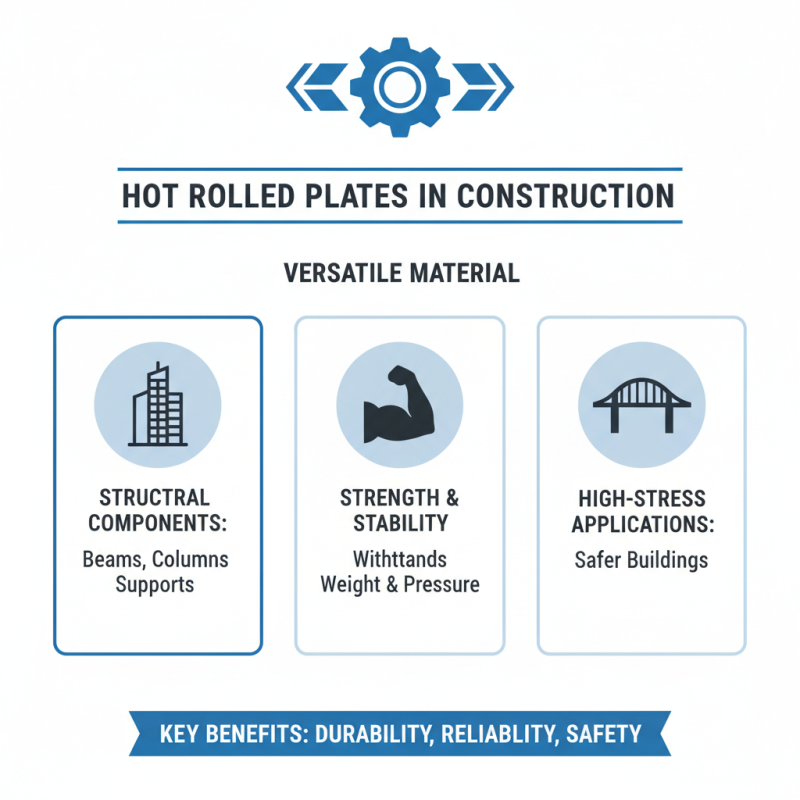
Hot rolled plates are highly versatile materials used in various industries. In construction, these plates serve as robust structural components, offering strength and stability. They are often used for beams, columns, and supports. The properties of hot rolled plates make them ideal for high-stress applications. They can endure significant weight and pressure, making buildings safer.
In manufacturing, hot rolled plates play a critical role. They are commonly used for creating machinery and equipment. These plates can be easily shaped and welded, allowing for intricate designs. This adaptability is essential for producing complex parts required in modern technologies. However, achieving the desired finish can sometimes be challenging. Companies must pay careful attention to the specific requirements for each application.
Moreover, the automotive industry utilizes hot rolled plates extensively. These plates are ideal for vehicle frames and chassis parts. Their durability ensures that vehicles can withstand rigorous conditions. However, it's essential to consider the environmental impact of production. Companies are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices. Balancing performance and sustainability is a critical challenge in today’s market.
Hot rolled plates are widely used in various industries. They are known for their durability and flexibility. One of the main advantages is their cost-effectiveness. When produced, hot rolled plates require less processing than cold rolled options. This makes them a preferred choice for large-scale structural applications.
Another benefit of hot rolled plates is their ability to undergo further processing. They can be easily welded and shaped into different forms. This versatility is valuable in the construction and manufacturing sectors. However, the surface finish of hot rolled plates may not be as smooth. Some users may find this a drawback for specific applications.
Hot rolled plates are also less prone to cracking. This quality is due to the heating process that allows for better workability. It is essential to consider the specific needs of a project. Not all applications require the advantages of hot rolled plates. Reflecting on the intended use is crucial for choosing the right material.
When selecting hot rolled plates for your projects, consider several key factors. The thickness of the plate can significantly impact its structural integrity. Thicker plates often provide better strength, but they can be heavier and more challenging to handle. Additionally, the width and length of the plate matter. Ensure the dimensions fit your project's requirements without excessive waste.
Material composition is another vital aspect. Different grades of steel have unique properties. Understanding these can help you choose the best type for your needs. For instance, some grades offer better weldability while others might resist corrosion. It’s essential to match the material to the specific conditions of your project.
Budget considerations are inevitable. Hot rolled plates can vary widely in cost. Sometimes, opting for a cheaper material might lead to issues later, such as warping or reduced performance. Weighing short-term savings against long-term durability is crucial. Reflecting on these choices can make a significant difference in your project's success.