Hot Rolled Plate is a crucial material in various industries. According to John Smith, a leading expert in the metal industry, "Hot Rolled Plate plays a vital role in manufacturing and construction." This versatile product offers strength and flexibility, which many sectors rely upon.
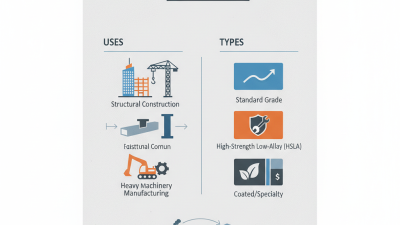
In construction, Hot Rolled Plate is used for beams and columns. It gives structural support that many buildings and bridges need. The plate is also favored in manufacturing processes. It is often shaped into machinery components. However, not all uses maximize its potential.
While Hot Rolled Plate has numerous advantages, there are challenges. The surface finish might not meet aesthetic needs. Some industries require additional treatment. Reflecting on these aspects helps optimize the use of Hot Rolled Plate. The balance between utility and appearance is essential for industry success.
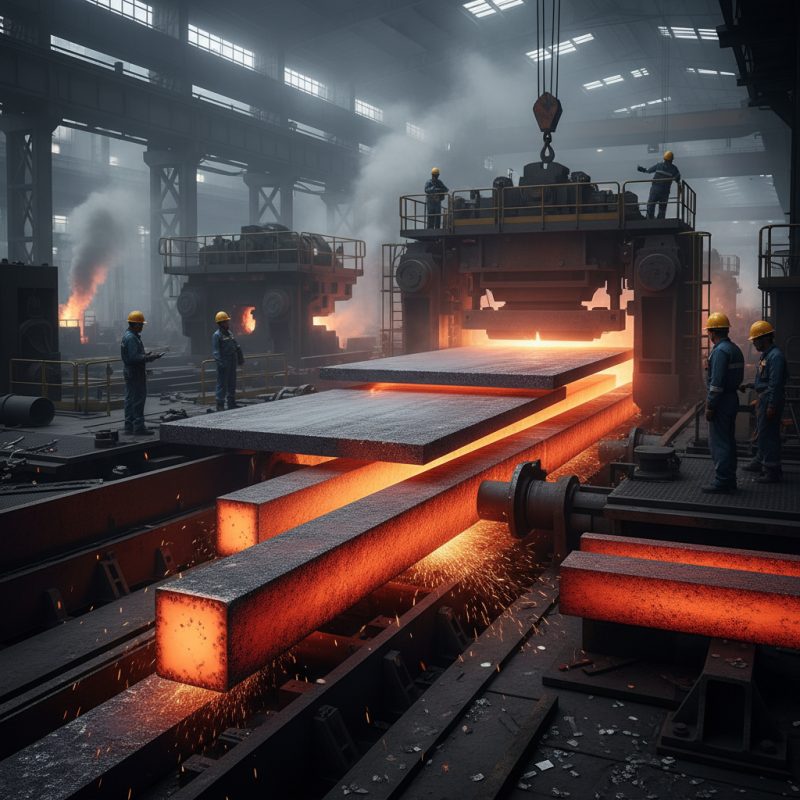

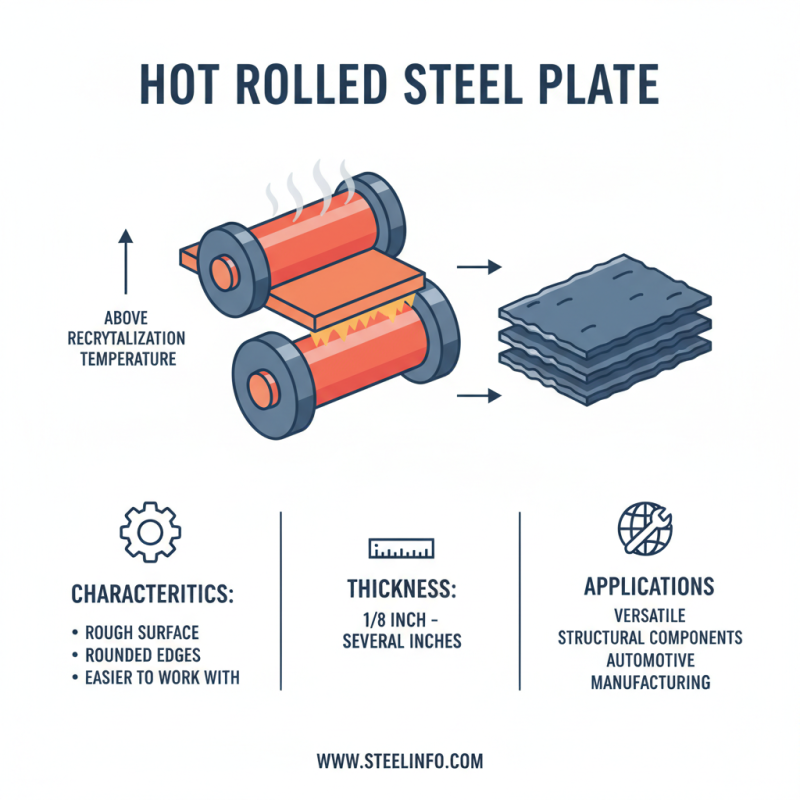
Hot rolled plate is a type of steel product known for its unique characteristics. The process involves heating the metal above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it to achieve desired thickness. This method gives the plate a rough surface and rounded edges, often making it easier to work with. The thickness typically ranges from 1/8 inch to several inches. The end product is highly versatile and widely used.
One of the defining traits of hot rolled plate is its malleability. It can be formed into various shapes without cracking. This property is essential for industries that require intricate designs or customized solutions. Additionally, hot rolled plates tend to have a lower cost compared to cold-rolled options. However, some might find the dimensional tolerance less precise. This is a consideration when working on projects that need exact specifications.
Another characteristic is its durability. Hot rolled plate is often used in construction and manufacturing. It can withstand heavy loads and harsh conditions. Despite this, the rough surface can pose challenges for some applications. It may require additional finishing when aesthetics are important. Users must reflect on these factors when choosing this material for specific tasks.
Hot rolled plate is produced through a specific manufacturing process that involves heating steel above its recrystallization temperature. The steel is then passed through large rollers to achieve desired thickness and flatness. This process allows for the material to be shaped more easily than cold rolling. The key equipment used in this method includes heavy-duty furnaces and rolling mills.
During the hot rolling, oxidation can occur on the surface of the steel. This can lead to imperfections that compromise the integrity of the final product. Additionally, achieving uniform thickness is challenging. Fluctuations in temperature or pressure can result in variances. Despite these issues, hot rolled plates are crucial for industries like construction and manufacturing.
The applications of hot rolled plates are diverse. They are often used for structural components, automotive parts, and shipbuilding. However, not all industries can rely on hot rolled plates for precision applications; some require tighter tolerances found in cold rolled plates. Evaluating the needs of a specific project is essential. Choosing the right type of plate can be complex and should not be overlooked.
Hot rolled plates are integral in many sectors. Their production involves heating steel above its recrystallization temperature. This process enhances its workability. The result is a strong and malleable material with various applications.
In the construction industry, hot rolled plates serve multiple purposes. They create structural components like beams and columns. These elements withstand significant weight and stress. According to a report by Global Steel Demand, the construction sector accounts for nearly 50% of the total hot rolled plate consumption. Engineers consider these plates for their strength and flexibility.
Manufacturing also heavily relies on hot rolled plates. They are essential for making machinery and equipment. In fact, about 40% of all hot rolled plate use comes from this sector, as per recent data. Companies use them in the production of automotive parts and appliance casings. However, the challenge lies in controlling quality. Variability in production can lead to defects. Regular quality assessments are vital to ensure the usability and integrity of hot rolled plates.
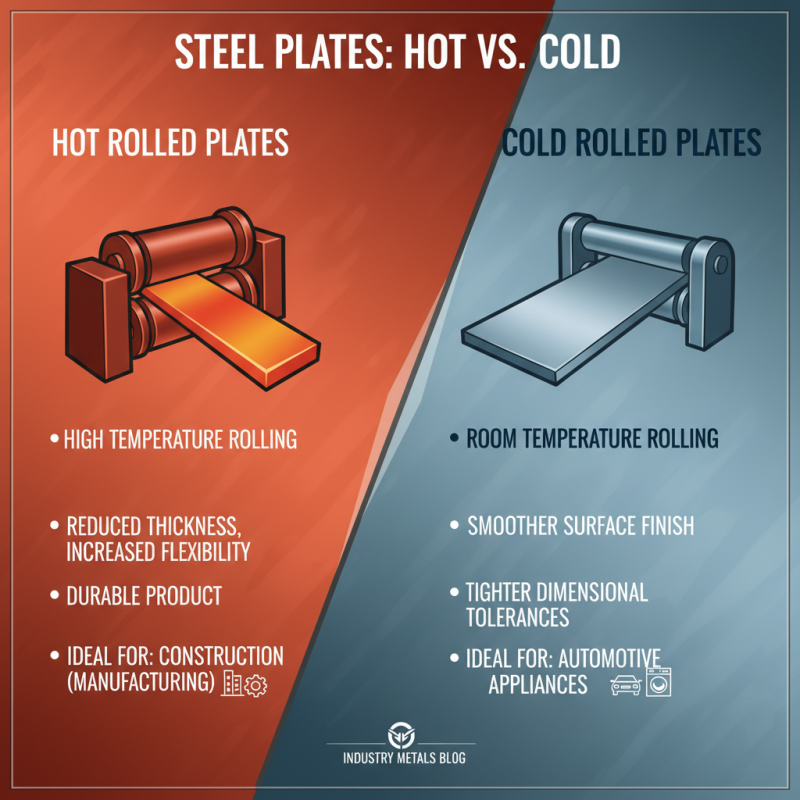
Hot rolled plates and cold rolled plates serve different purposes in various industries. Hot rolled plates are made by rolling steel at high temperatures. This process reduces thickness and increases flexibility. The result is a durable product, ideal for construction and manufacturing.
Cold rolled plates are produced at room temperature. This method yields a smoother finish and tighter tolerances. While hot rolled plates are often less expensive, cold rolled options provide better surface quality. This distinction is crucial when selecting materials for specific applications.
Tip: Consider the end use of the product. For structural applications, hot rolled plates are often preferred for strength. However, for aesthetic needs or intricate parts, cold rolled plates hold an advantage.
When choosing between these two types, think about the project requirements. Hot rolled plates can warp during cooling. This may affect precision. Cold rolled plates avoid that issue but come at a higher cost. Weighing these factors is essential for optimal results.
Tip: Always consult with a material specialist before finalizing decisions. Their insights can help prevent costly mistakes.
Hot rolled plate is widely used in various industries. It is known for its malleability and ease of fabrication. However, the decision to use hot rolled plates comes with both advantages and limitations, especially in construction.
One significant advantage is the cost-effectiveness. Hot rolled plates are generally less expensive than their cold rolled counterparts. They can be manufactured quickly, making them ideal for large-scale projects. The surface finish is often rough, which may not be appealing but offers excellent mechanical properties. Despite this, some projects demand a more refined finish, which hot rolled plates do not offer. The thickness can also vary significantly, which could lead to challenges in certain applications.
On the other hand, there are notable limitations. Hot rolled plates can have residual stresses due to the manufacturing process. This can lead to warping or distortion under specific conditions. Additionally, the dimensional tolerance is less stringent. This aspect might not suit projects that require precise measurements. Construction professionals must weigh these factors carefully. Understanding when to use hot rolled plates requires experience and caution.